PV knowledge
How Agriculture and photovoltaics
Can go hand in hand
Almost all solar parks are built on agricultural land. This applies to both agri-photovoltaics and conventional solar parks. In agrivoltaics, productive agriculture is realised under and next to solar modules. However, land must also be cultivated in traditional solar parks.
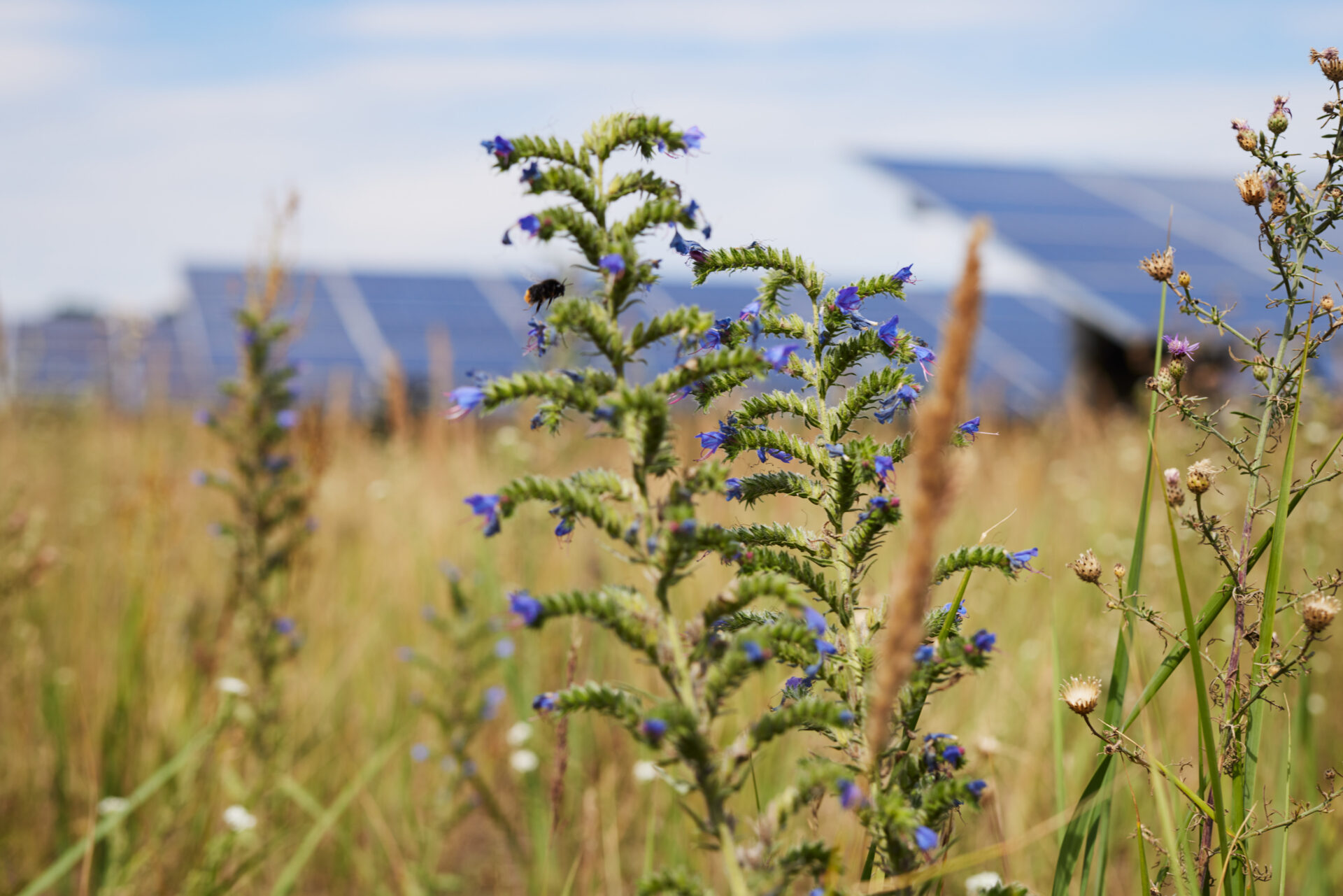
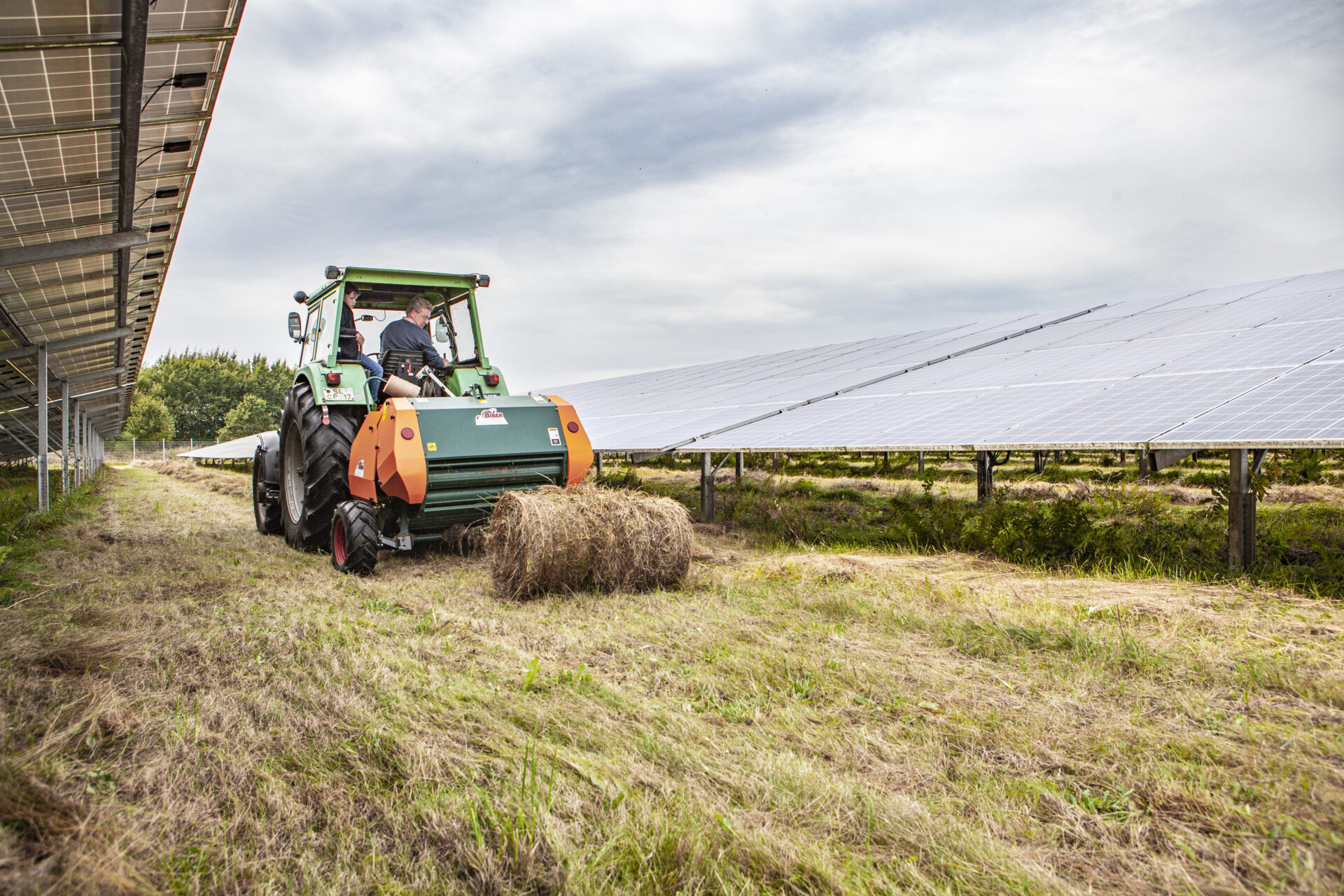
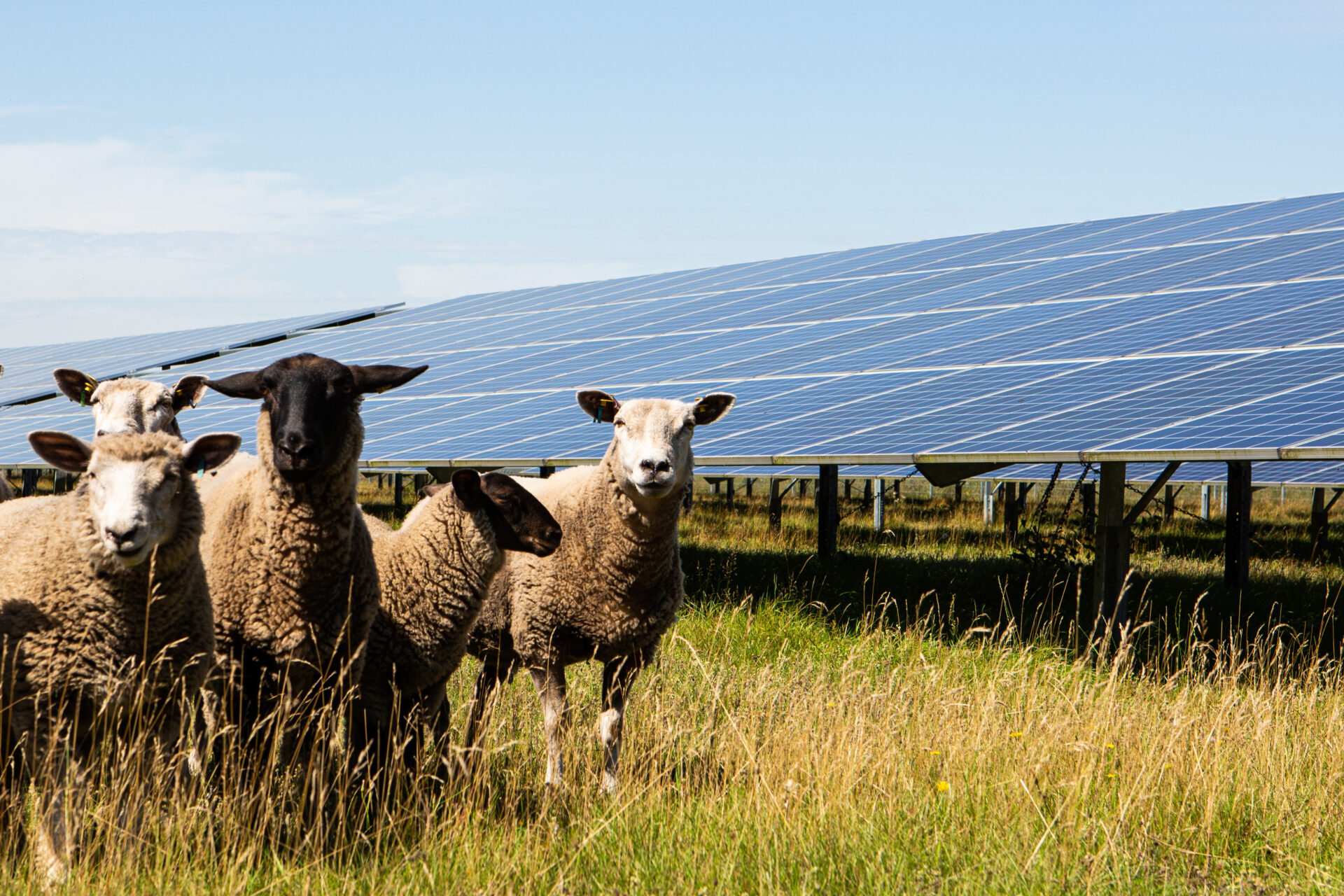



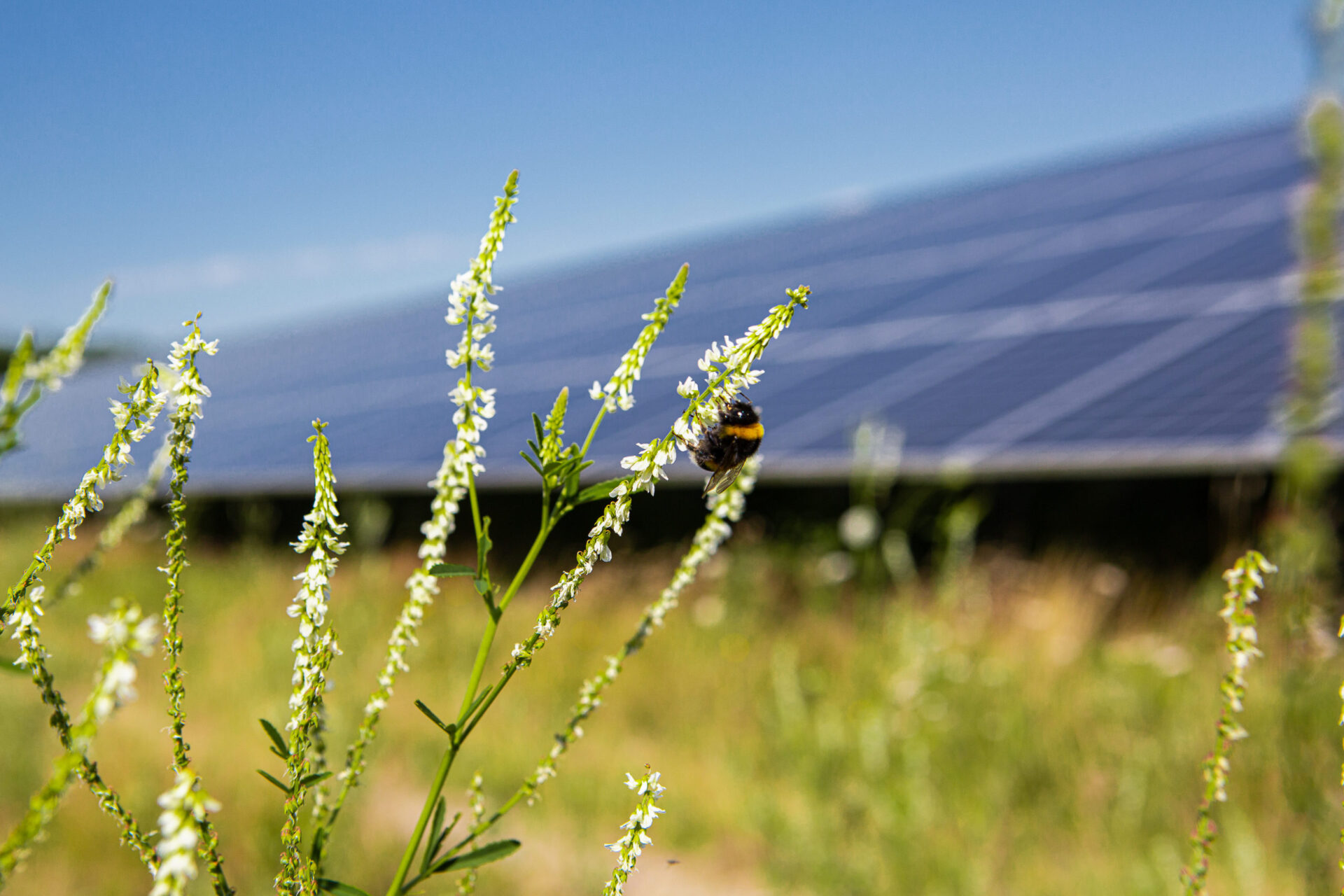
Solar parks are being built on agricultural land
Almost all solar parks are erected on agricultural land. This concerns both Agri-photovoltaics as well as classic solar parks. In agri-photovoltaics, productive agriculture is realised under and next to solar modules. In classic solar parks, areas must also be cultivated. Although many farms want to secure their income from photovoltaics, they do not want to jeopardise the preserve the agricultural value of their land.
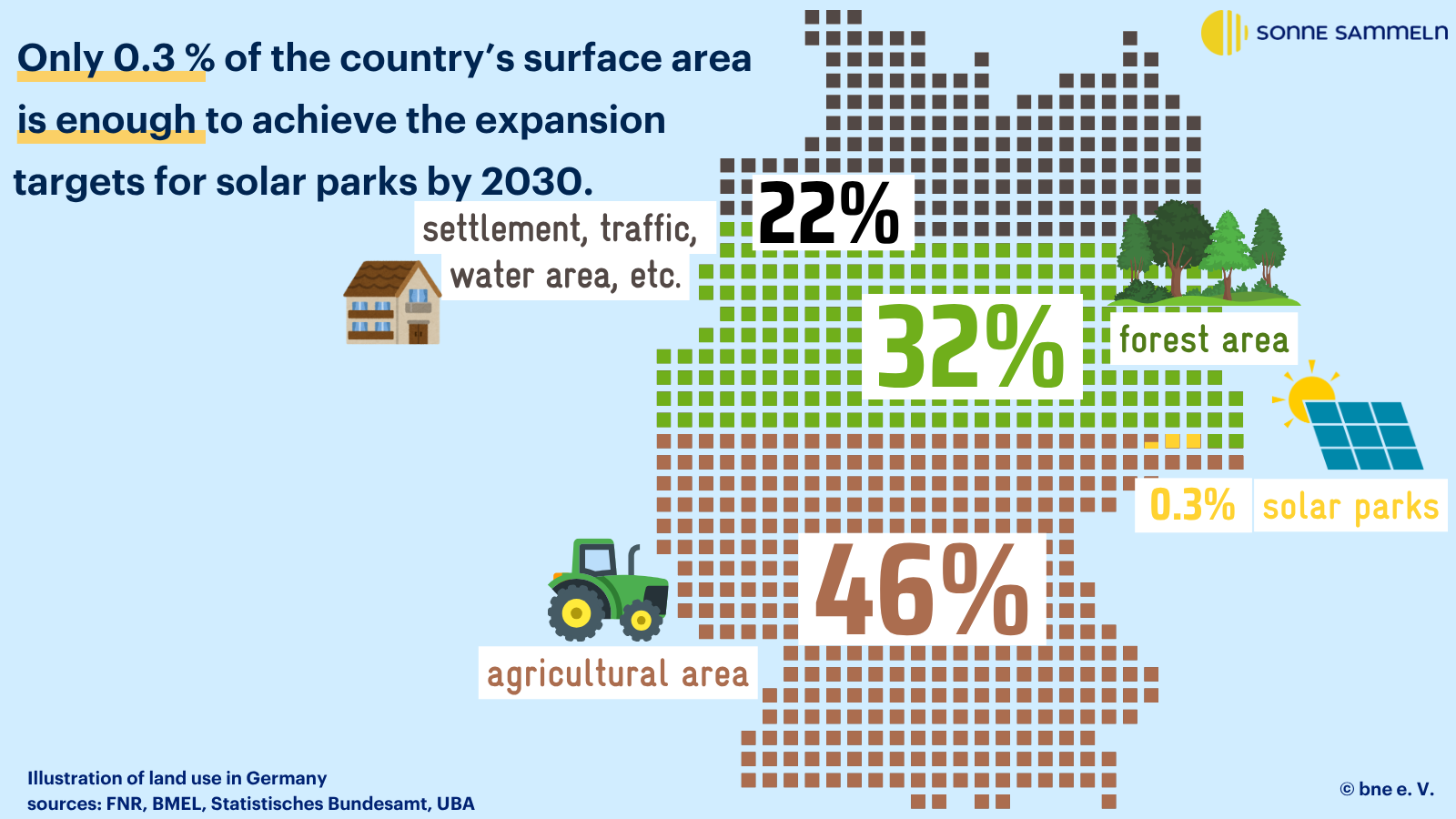
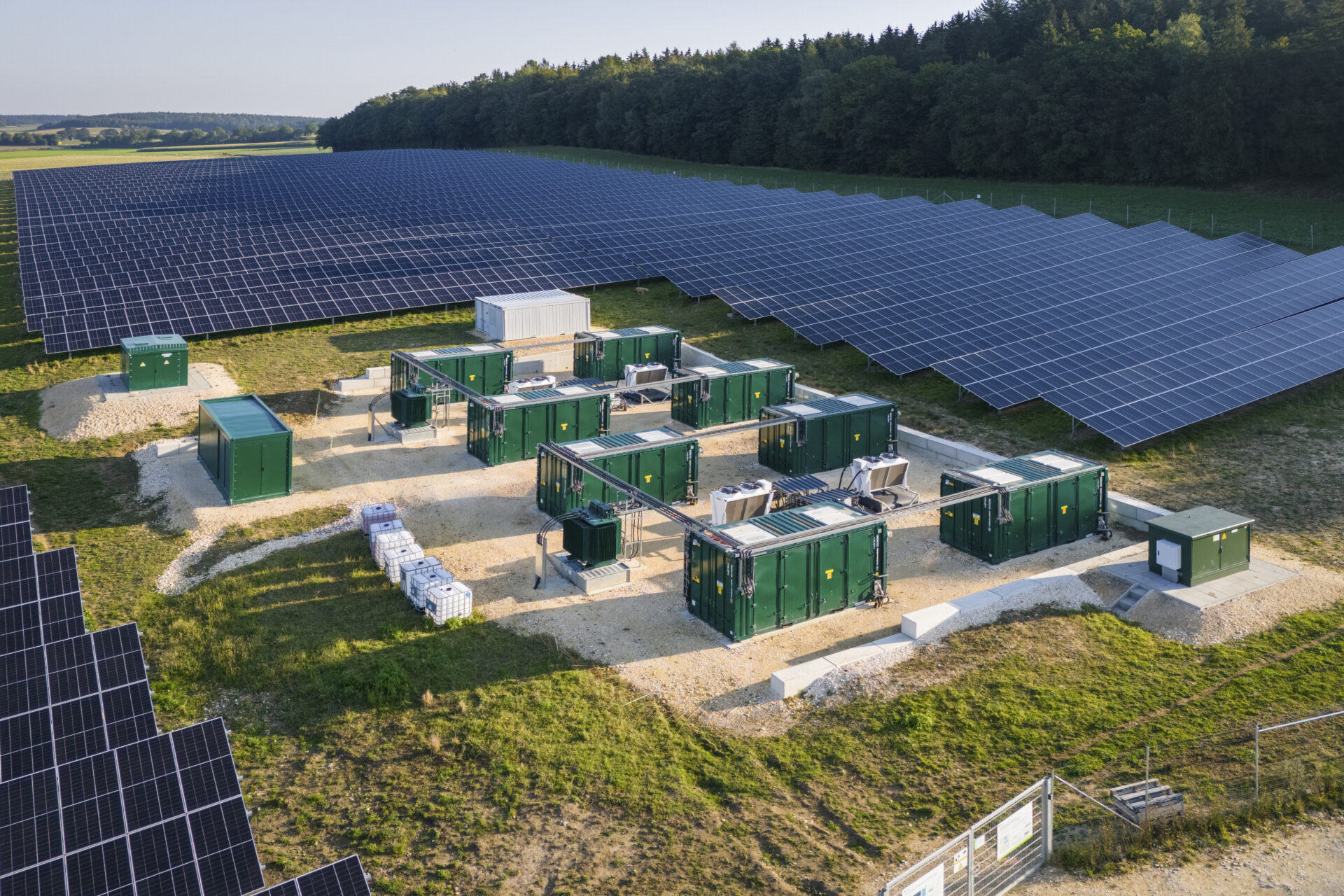
By 2030, solar parks will require around 0.6% of agricultural land in Germany - a small proportion compared to other forms of land use, see also charts below. As the foreseeable Most of the expansion in classic solar parks and these will increasingly be serve biodiversitymeasures are necessary. It is important that the Expansion of solar parks better suited to agriculture in futureeven if the solar park areas are professionally managed for biodiversity.
Important facts about agriculture & photovoltaics
On our PV knowledge pages you will find important information in simple language on topics that are currently being discussed in politics and business. We would be delighted if you would share the fact sheet with your network!
How much space do solar parks need?
area issue
Solar parks with an output of 27.3 GW have currently been installed in Germany, covering an area of around 40,000 hectares. The efficiency of PV modules is increasing every year. Current PV modules for solar parks now achieve efficiencies of 24% and more. This means that more power can be installed per area with the same construction method. Assuming that one hectare of land will be required per one MW of solar park in the future, this will result in a land requirement of around 12,000 hectares per year by 2030. A large proportion of this land will be agricultural land.
To achieve this Space requirements in context To illustrate this, we have visualised the distribution of land in Germany: 46% of the land in Germany is used for agriculture, 16.6 million hectares to be precise. The remaining area is taken up by settlements, transport, water and forests.
Important facts about agriculture & photovoltaics
Download now
How agriculture and photovoltaics can go hand in hand (only in German)
Ratio of PV-FFA to Agri-PV
Which solar parks utilise agricultural land?
Almost all solar parks utilise agricultural land. The majority of these are classic ground-mounted PV systems. Agri-PV systems are only being built on some areas.
The diagram on the left shows the differences and similarities between the two solar park variants. One thing is clear: at least 80% of the PV ground-mounted expansion path according to the EEG is covered by ground-mounted PV systems.
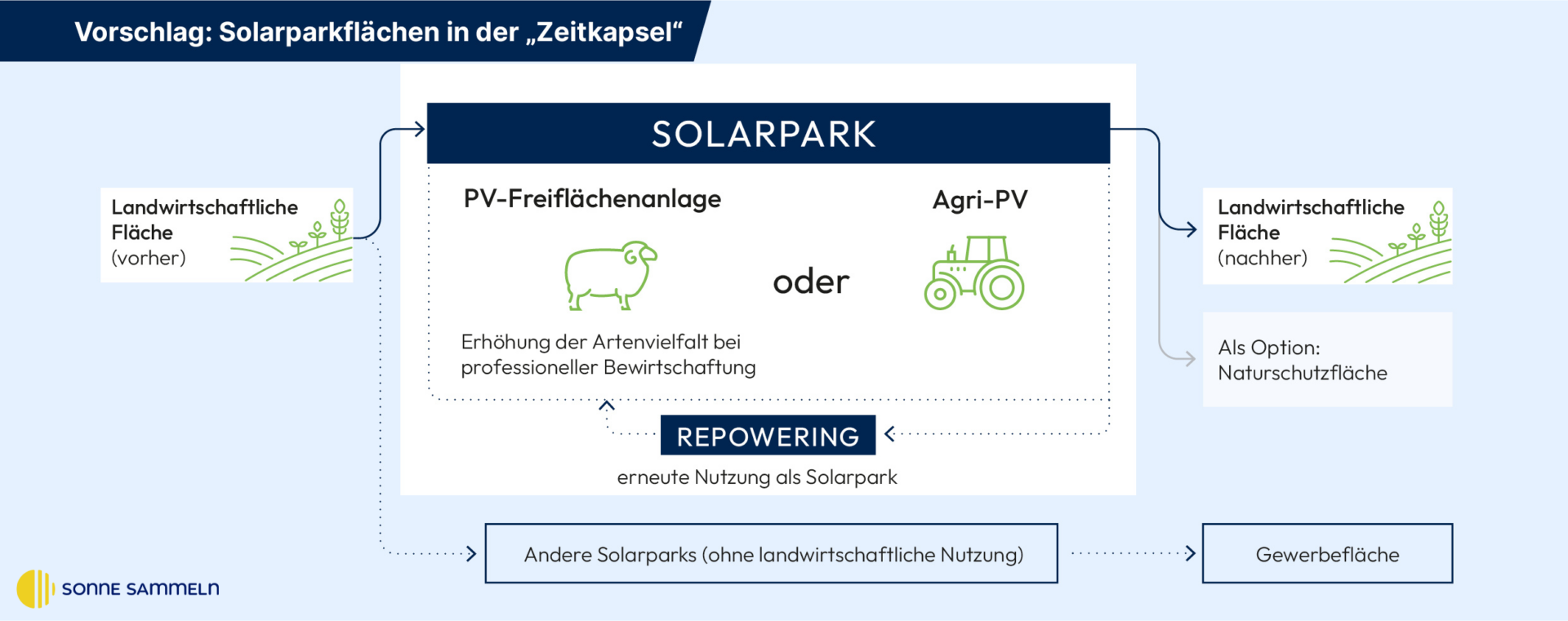
Proposal:
Solar parks as a time capsule
If land management in species-rich solar parks were recognised as agricultural use, this would solve many problems for farms. From the farm's point of view, these areas would go into a kind of time capsule: Areas in the solar park would be an interim agricultural use (species-rich solar park) and can then be used for agriculture again. The land would retain its agricultural status and value. status and value. This would also reduce tax risks for agricultural businesses, but only in species-rich solar parks.
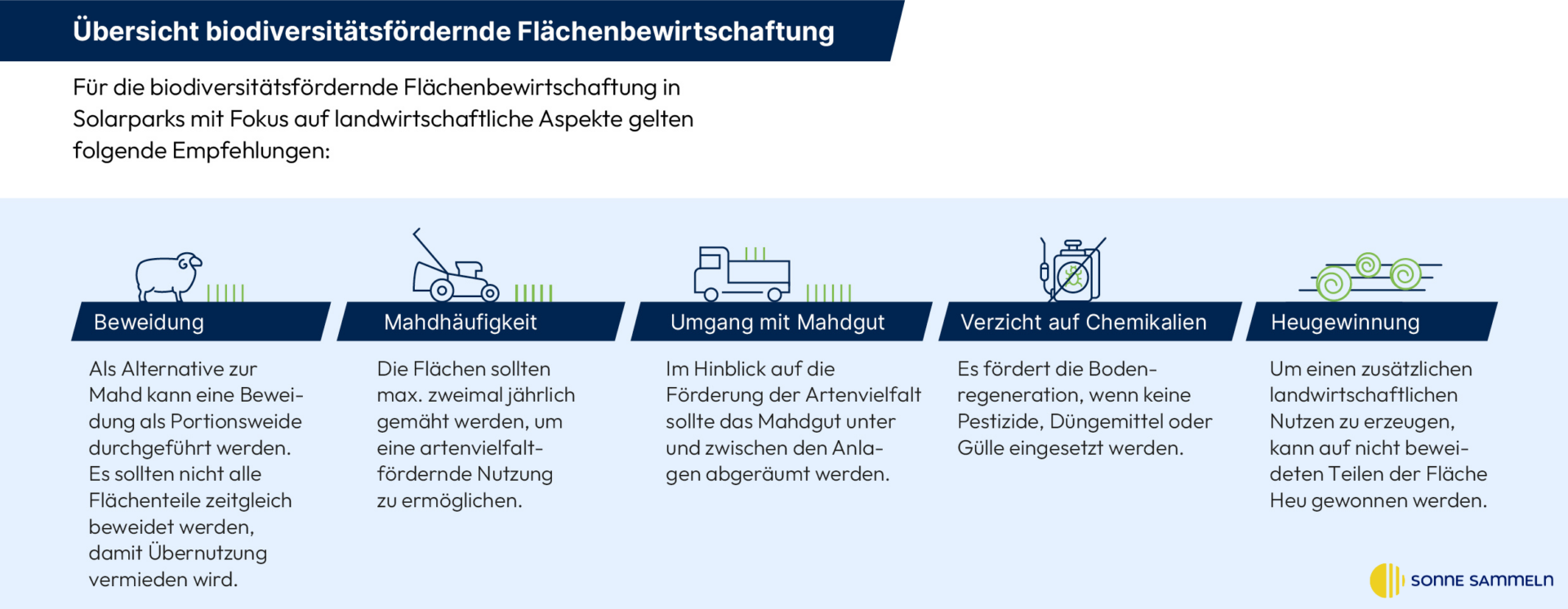
Recommendations for land management that promotes biodiversity
Overview of the measures
In well planned and properly managed Solar parks form species-rich grasslands. This increases the Insect diversity strong. This forms the Food source for birds and other species groups. The result is a Important habitat for animalssecured for decades by the solar park. The professional and correct management of the land is crucial for this mechanism.
Win-win-win situation for energy,
Agriculture and nature
Holger Reimer
Farmer in Schleswig-HolsteinFor me, the solar park is a secure pension scheme and a stable foundation stone for the next generation. (...) It's a good feeling to know that the area, which has undergone so much change, now has a meaningful purpose for at least the next 20 years.

More PV knowledge
On our PV knowledge pages you will find important and in-depth information in simple language on current topics that are currently being discussed in politics and business. A suitable fact sheet on the respective topic is available for download on the respective page.

© BayWa r.e. 
© Wattmanufactur 
© EnBW/Paul Gärtner