PV knowledge
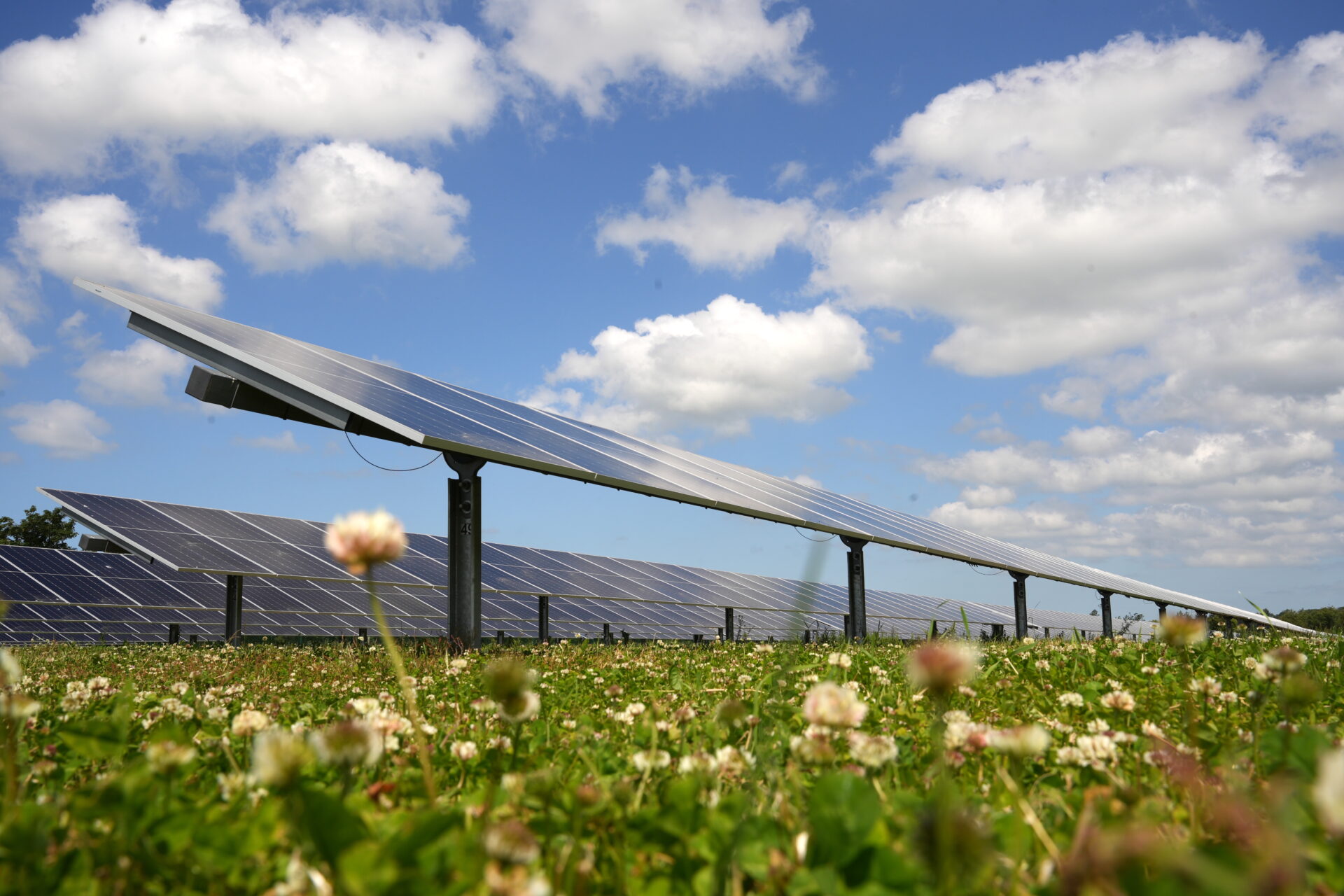
Solar parks as an opportunity for the Biodiversity
The Bundesverband Neue Energiewirtschaft e.V. (bne) is analysing biodiversity in modern solar parks throughout Germany. The research took place in summer 2024 and has now been published in a comprehensive publication.



Findings of a nationwide field study and recommendations
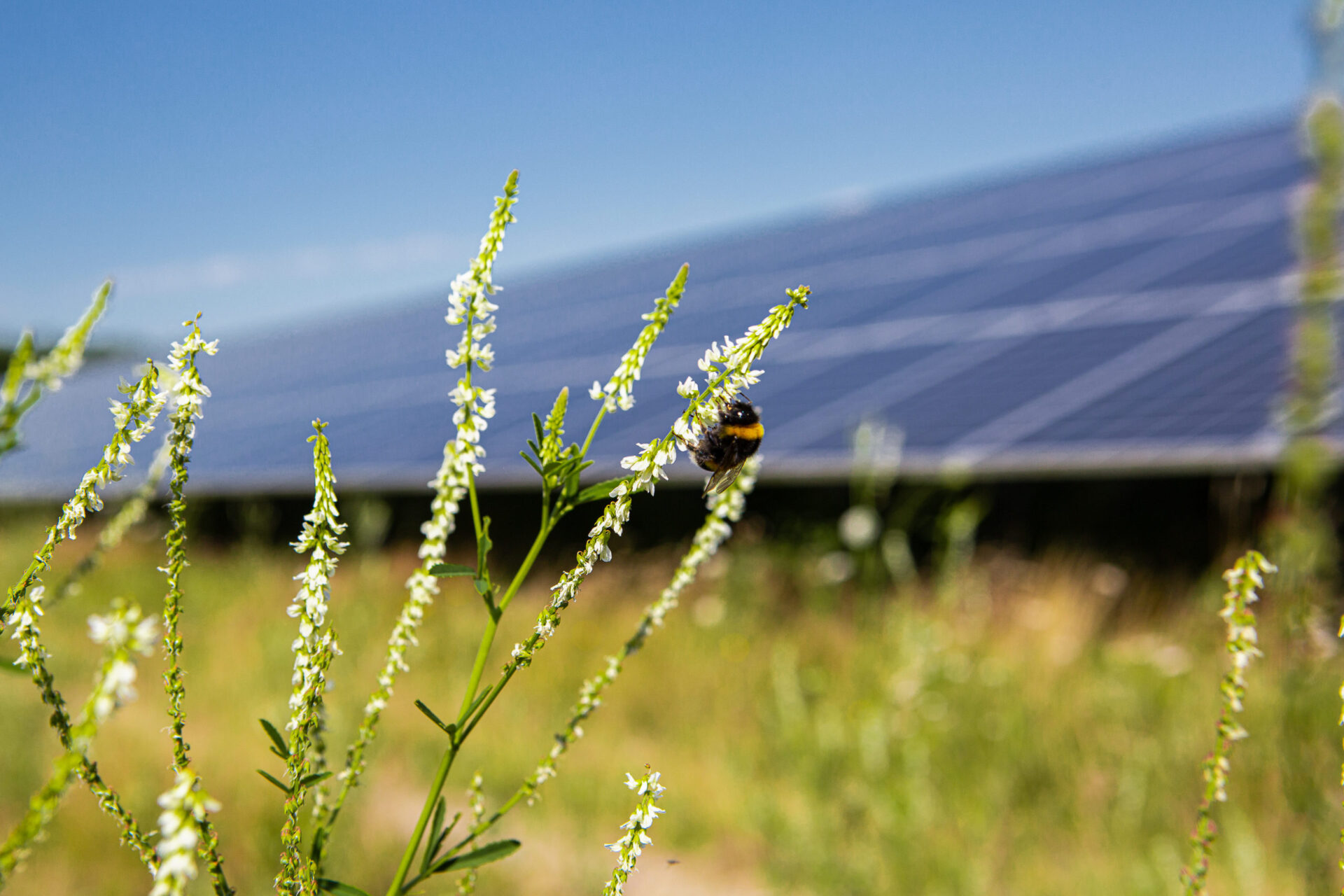
Solar parks are an important component of our modern energy system. They enable a Safe, quickly realisable and clean energy generation with predictable costs for electricity production over several decades. Well-planned solar parks have another advantage - their value for biodiversity in our agricultural landscape. They are able to positive contribution to environmental protection and nature conservation to perform. The Study "Biodiversity in solar parks - a nationwide field study" makes this value tangible and provides findings that are likely to be of great relevance for the nature conservation assessment of solar parks.
Insight into the study: structure and focus
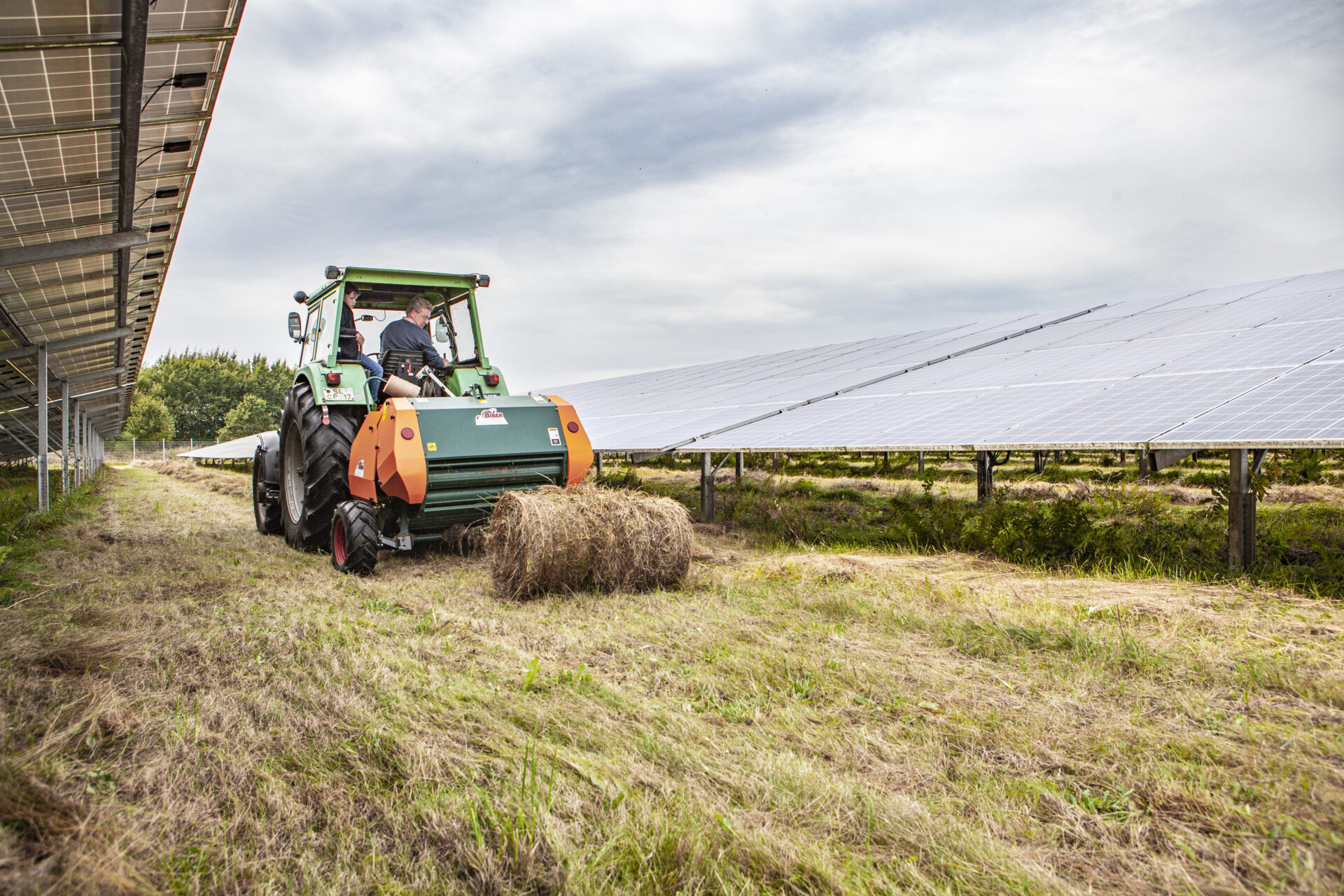
In the study, biodiversity surveys were carried out and analysed at 29 solar parks across Germany. The focus of the surveys was on solar parks that are located on land formerly used for agriculture which corresponds to the expansion focus both in the EEG tender and in the PPA segment.
In the individual solar parks, eight species groups were recorded several times in 2024 by the study authors and specialised expert offices in over 100 individual surveys:

In particular, the botanical features and structural elements relevant to biodiversity were recorded at all solar parks. Other randomly recorded species supplemented the collected data so that the biologists were able to analyse a total of more than 550 species were able to identify. The study also takes into account current studies and information provided by the operators, for example on the maintenance or construction of the systems. "Biodiversity in solar parks" is an update of the bne biodiversity study from 2019, which at the time significantly shaped the topic of biodiversity in solar parks.
Important facts about biodiversity in solar parks
Download now
German
Solar parks as an opportunity for biodiversity (only in German)
English
Solar energy presents an opportunity for biodiversity
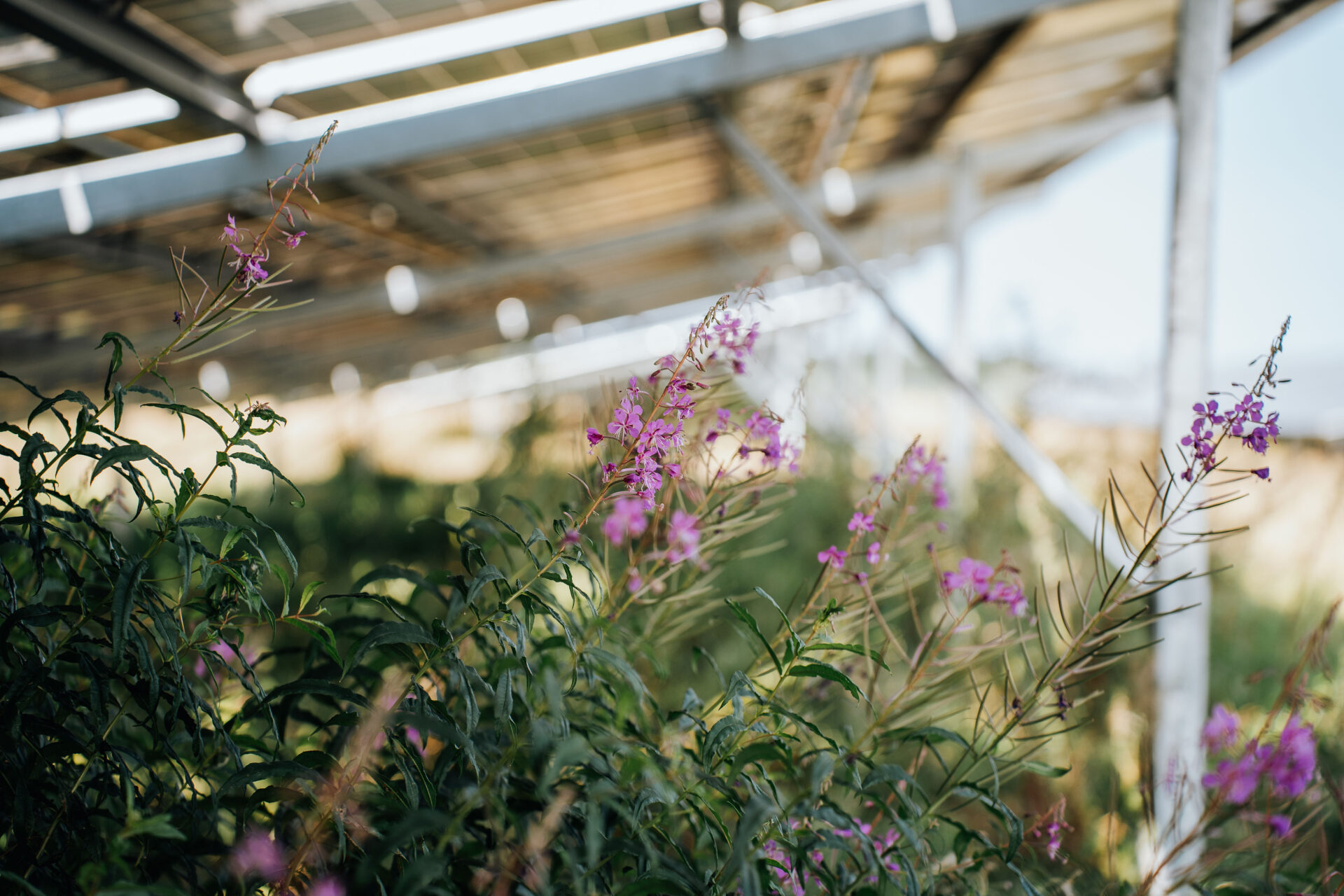
Animals discover solar parks as habitats and feeding grounds
findings from the study
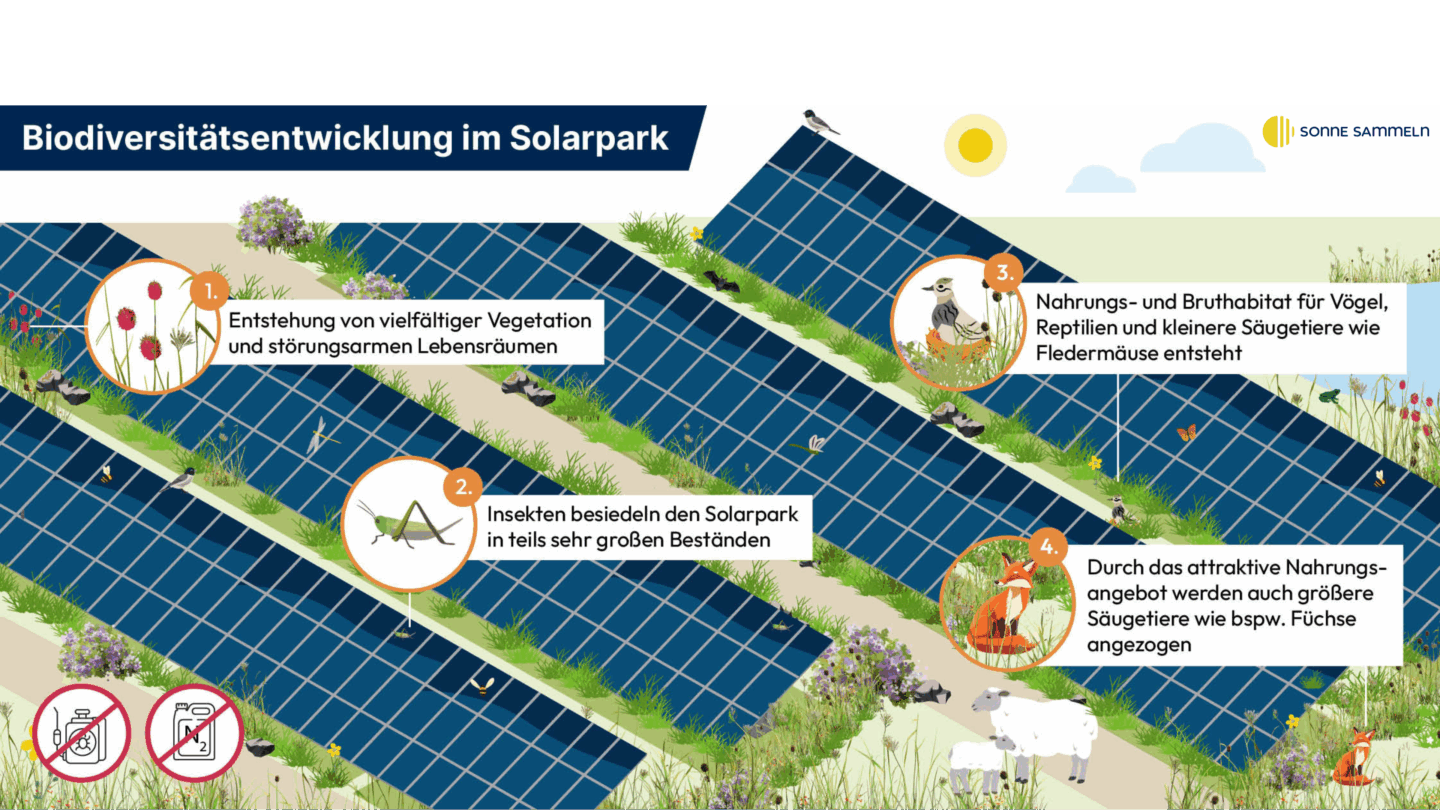
Another finding from the study concerns the learning ability of animals such as birds and bats. The increase in flower-rich vegetation produces an attractive food supply in the form of insects in the ground-mounted PV systems, which attracts these species groups.
In the midst of a landscape characterised by agriculture, solar parks form low-disturbance structures and maintain them for decades. The result is a learning effect: the animals learn that they can use this comparatively new environment as a feeding and breeding habitat.
Importance of biodiverse solar parks for politics and the economy
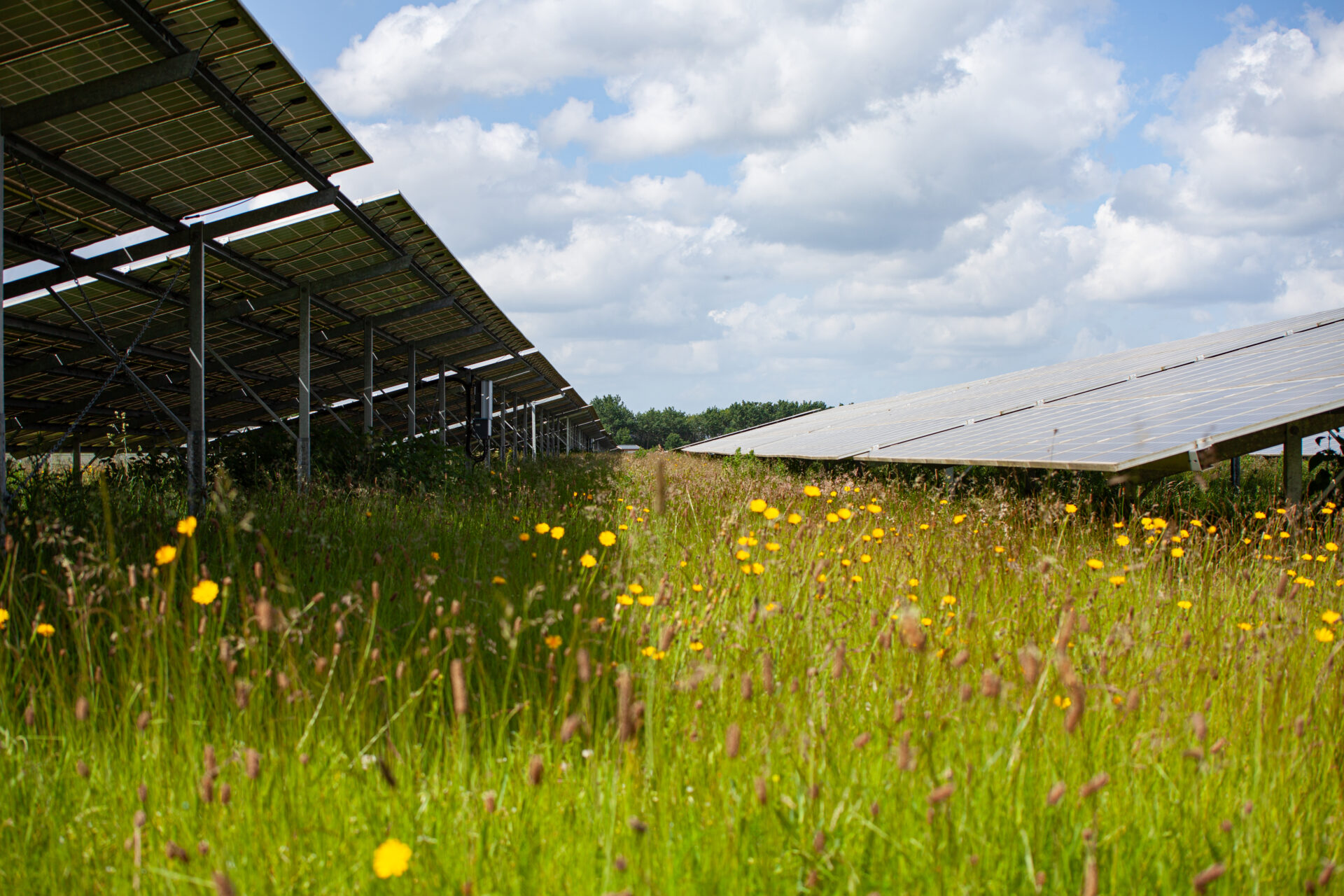
Low-disturbance areas
"Biodiversity in solar parks - a nationwide field study" confirms the value of well-planned solar parks for biodiversity. The species created in the plants low-disturbance areas offer rare and endangered species valuable habitats.
This is one of the reasons why they fulfil similar criteria to the "High-Nature-Value Farmland" and should therefore also play a role in the implementation of the National Strategy on Biological Diversity 2030 play. No funds would have to be made available from the federal budget for this measure. Solar parks are relevant for achieving several goals - this should also be reflected in planning practice and land utilisation. In order to to make species-rich solar parks the standardproject developers need planning certainty and landowners need risk protection, for example in that the Agricultural land status retained remains.
PV knowledge: Facts and trends in solar park expansion
In our knowledge portal you will find information on current topics and trends in solar parks and battery storage that are currently being discussed in politics and business. For each topic there is a suitable fact sheet to download.

© Wattmanufactur 
© BayWa r.e.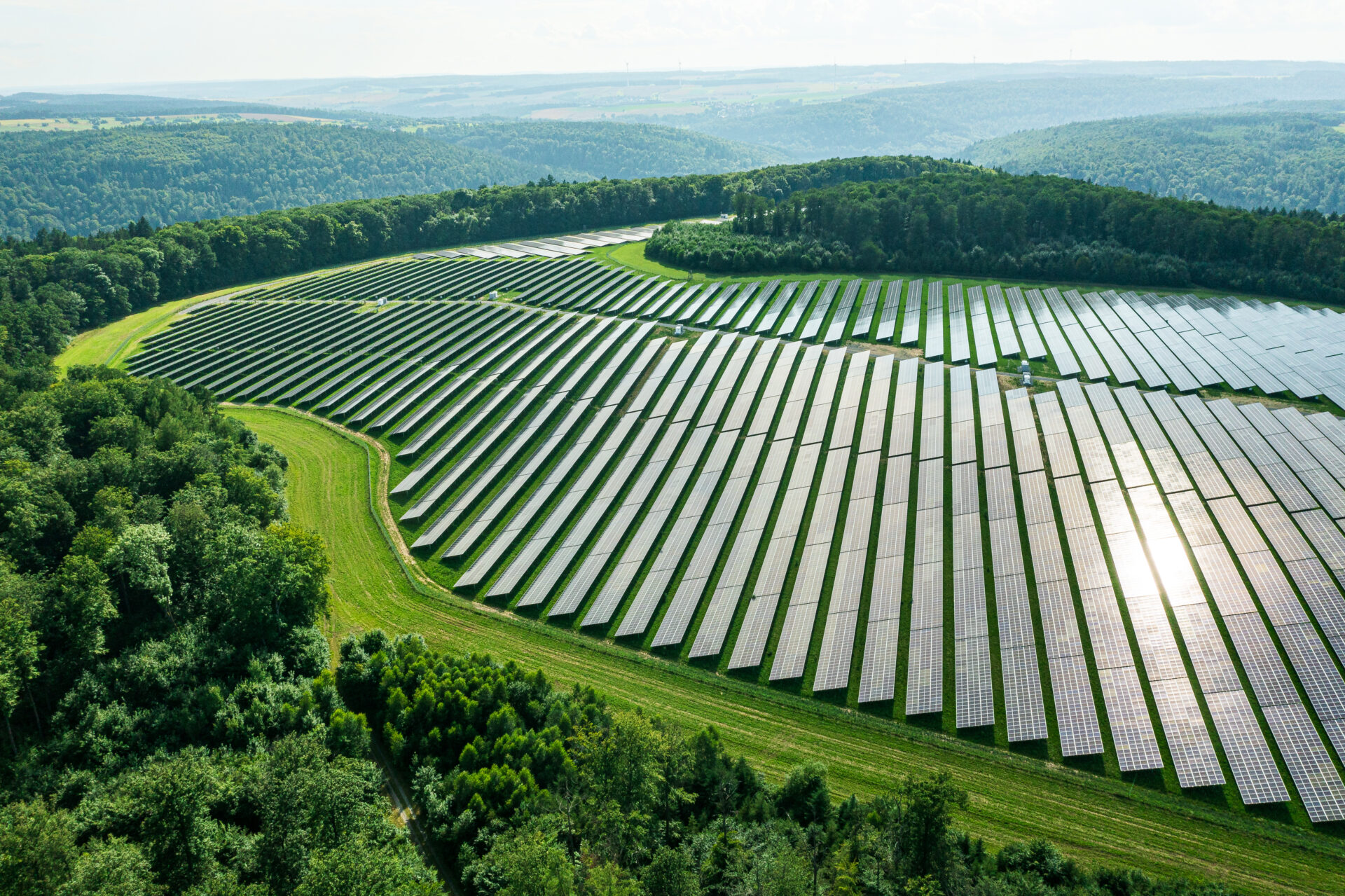 
© EnBW/Paul Gärtner