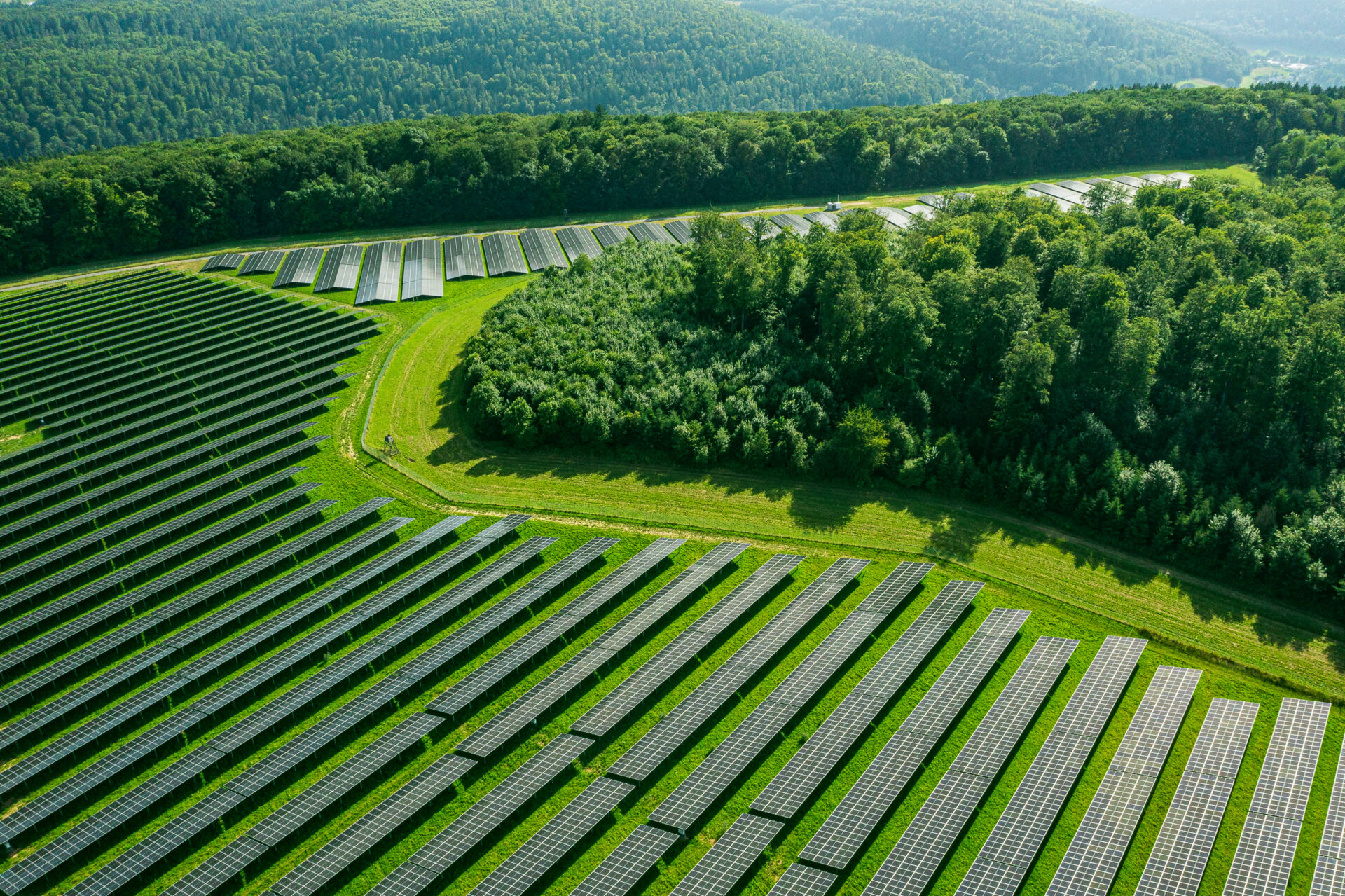
How much space is needed when the Expansion targets for photovoltaics are to be achieved? On which surfaces are there solar parks? What proportion of solar park areas of Germany's total area? These questions will be addressed in this article.
Contents
- What expansion targets for solar energy is the German government pursuing?
- How much space will be needed for future solar parks?
- What is grown on the agricultural land?
- How are solar park areas managed?
- What effect do solar parks have on the land?
- How are solar parks recorded in the area statistics?
- Conclusion
What expansion targets for solar energy is the German government pursuing?
Germany is to be Completely climate-neutral by 2045 manage. This means, among other things, that Climate Protection Act. In order to achieve this target, renewable energies must account for at least 80% of gross electricity consumption by 2030. Photovoltaics plays an important role in this, as solar energy is one of the most most cost-effective energy source. Correspondingly The expansion plans are progressiveWe need an additional 215 gigawatts (GW) of solar power by 2030. The outlook is good: in 2023, the expansion target of 9 GW was exceeded by around 6 GW. Now 13 GW are to be added in 2024, 18 GW in 2025 and 22 GW annually from 2026. Of this, the Half for ground-mounted systems and roof systems, according to the plan in the EEG.

How much space will be needed for future solar parks?
One piece of good news first: Germany has Sufficient area for renewable energy sources.
Solar parks with a capacity of 27.3 GW have currently been installed in Germany (as of September 2024, view via the Market master data register or OpenEnergy Tracker), which About 40,000 hectares claim. The efficiency of PV modules is increasing every year. Current PV modules for solar parks now achieve Efficiencies of 24% and more. This means that with the same design More power per area can be installed. Assuming that one hectare of land will be required per one MW of solar park in future, this results in a land requirement of approx. 12,000 hectares per year by 2030. A large proportion of these areas are Agricultural land be. There are several reasons for this: Firstly, agricultural land represents the largest proportion of land in Germany, see below. In most cases, low-yield locations are chosen that can generate additional income for landowners as solar parks. Secondly, the installation of PV modules on developed agricultural land is easier to realise from a structural point of view than in urban areas, for example.
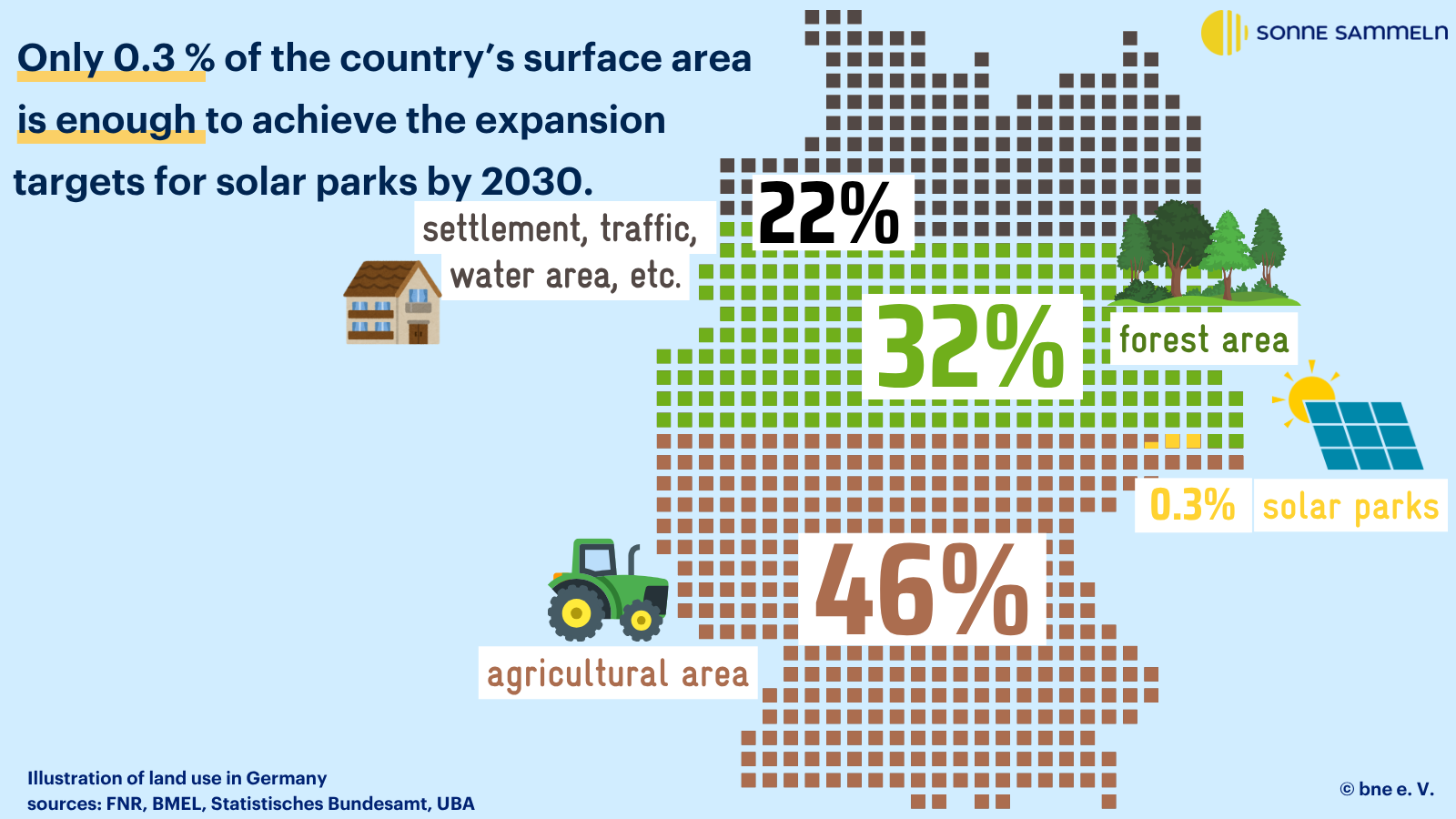
To put this demand for space into context, we have visualised the distribution of space in Germany: 46% of the land in Germany is used for agriculture. used, 16.6 million hectares to be precise. The remaining area is taken up by settlements, transport, water and forest.
Assuming that in 2030 around 95,000 hectares of land for solar parks would correspond to a share of approx. 0.3% of the total area of Germanycomparable to the size of the Island of Rügen.
What is grown on the agricultural land?
The 16.6 million hectares of land used for agricultural purposes are to 82% for feed and food production used to 13% become energy crops and on 2% industrial crops.
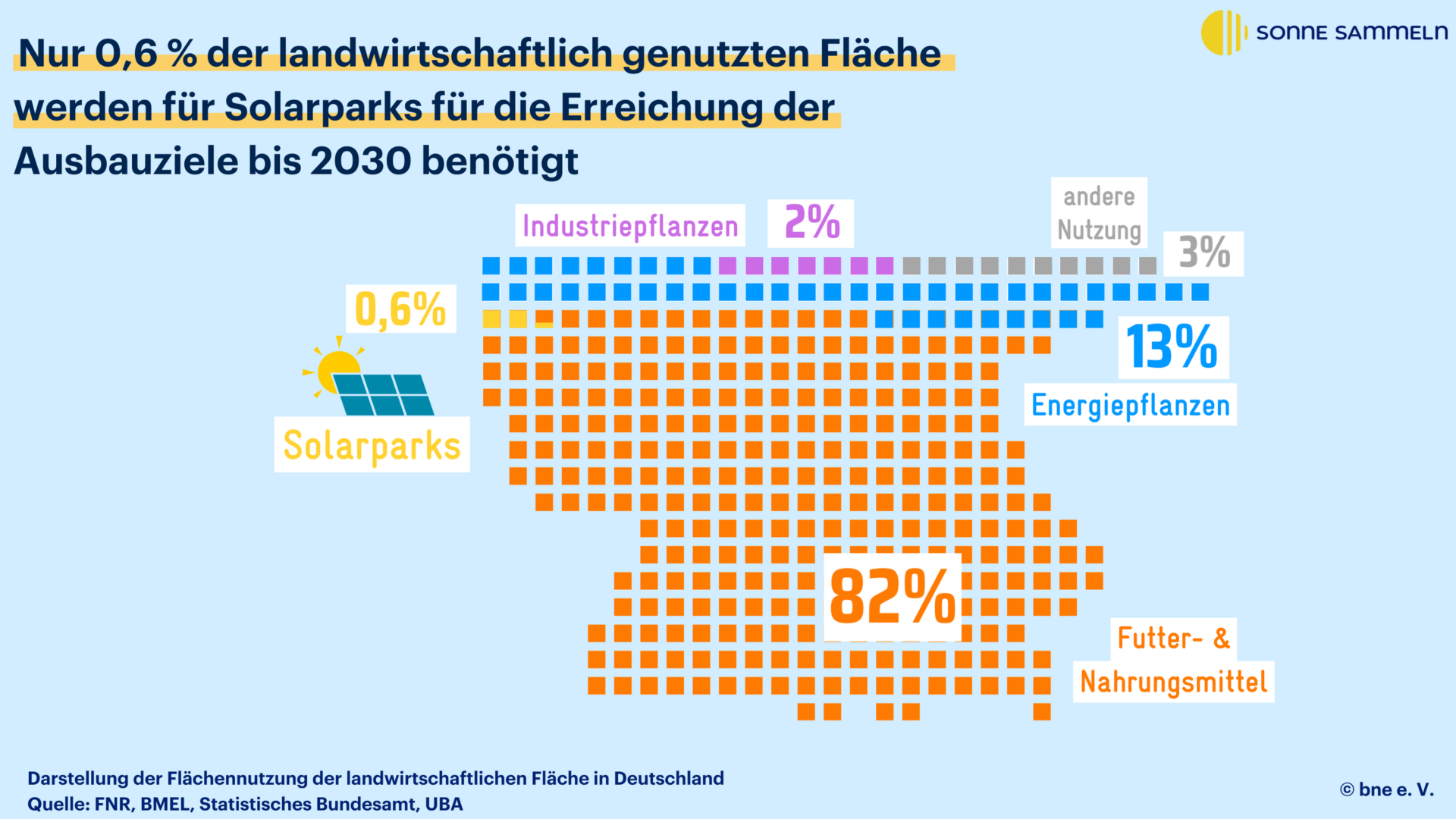
In order to achieve the expansion target for photovoltaics only about 0.6% of agricultural land with solar parks by 2030 are cultivated. This means that the proportion of land used for ground-mounted PV systems is far lower than for energy or industrial plants.
How are solar park areas managed?
The areas in the solar park are not only used to generate energy, but are also utilised in two or sometimes three ways. There are different land utilisation concepts in combination with photovoltaics. With the classic Agri-photovoltaics agricultural crops can be roofed over with solar modules, which in certain areas Valuable synergy effects can offer. Speciality crops such as apples, cherries or raspberries, which need to be protected from severe weather events, benefit to some extent from the Protective and shading effect of the modules.
Agri-PV concepts are currently being trialled. In the EEG call for tenders, up to 2030 around 7.8 GW of so-called "special PV systems" are planned, the majority of which are likely to be agrivoltaics. This means that agri-PV will account for a share of almost 14% by 2030.
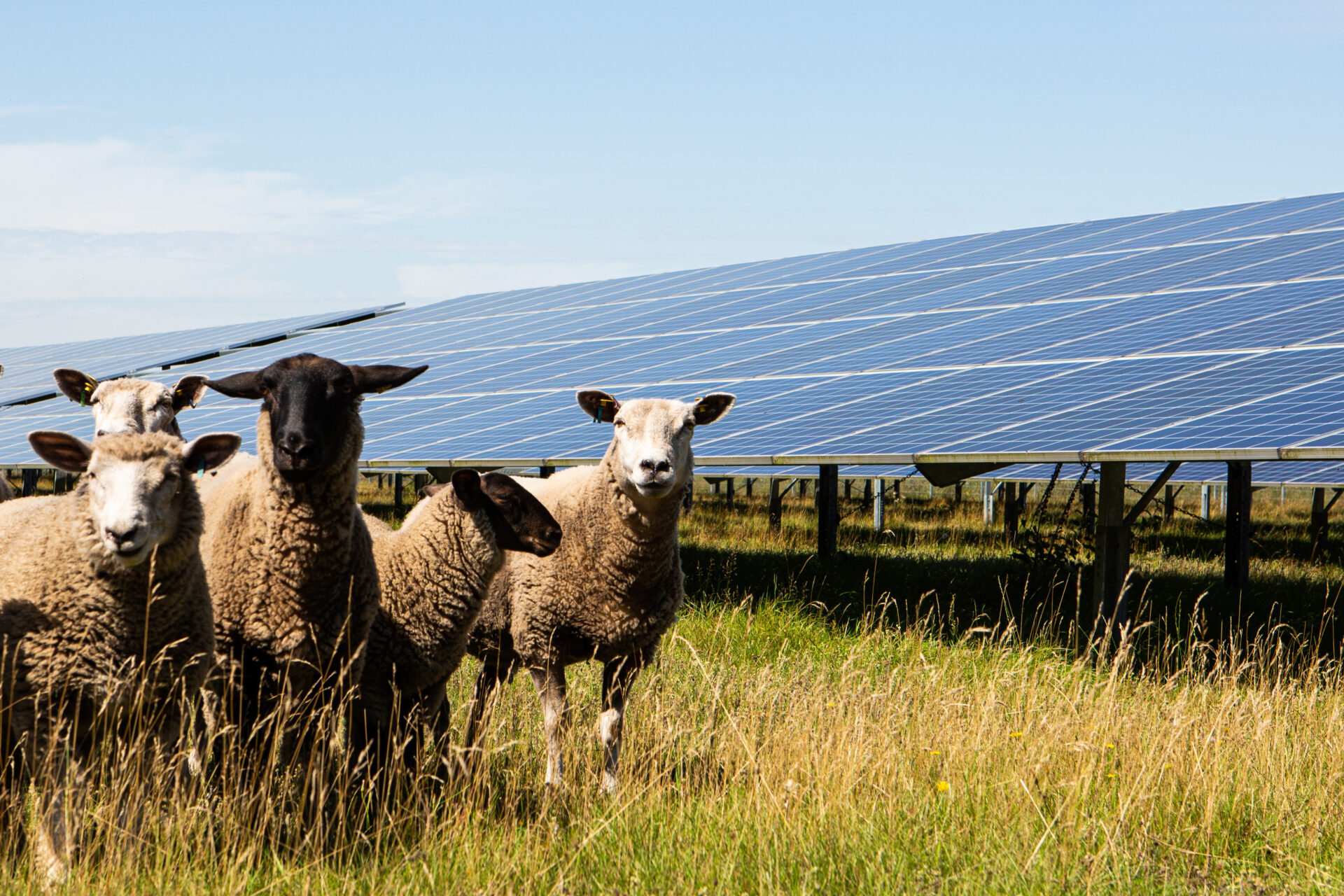
The The majority of new PV installations will be "conventional" ground-mounted systems which will also be built on agricultural land. Here, too, a Agricultural use of the land is common and advantageousbecause solar park areas also need to be professionally maintained and managed, e.g. by mowing or grazing with sheep. You can find out how area maintenance is implemented in solar parks here read in detail here. Solar park areas can have a triple advantage mean: Agricultural utilisation in the form of of pasture or grassland managementthrough a Increasing biodiversity compared to agriculturally utilised areas, and through the Production of clean, low-cost energy.
What effect do solar parks have on the land?
The Degree of sealing for solar park areas includes racks, inverters, storage and other ancillary systems under 2% of the area and is therefore very small. The areas are not fertilised or sprayedwhich is why species-rich vegetation can develop that Insects, reptiles and birds for feeding and nesting offers. The soil, which was previously mostly used for productive agriculture, can recover. Upgrading the soil quality takes place. A target can also be increased be humus formation. The sparing use of land in the solar park means that the Improved water retention capacity and reduced risk of erosion. Precipitation also reaches the built-up areas due to the gaps between the modules.

How are solar parks recorded in the area statistics?
In a densely populated country like Germany Space is a precious commodity. Nevertheless, according to statistics, in recent years daily Around 52 hectares for settlement and transport areas new areas - the equivalent of around 72 football pitches a day. According to the German Sustainability StrategyIn line with the targets formulated in the strategy, only a maximum of 30 hectares per day should be newly designated as settlement and transport areas in the years up to 2030. In particular, the Protection and conservation of agricultural land in the foreground.

Areas with Ground-mounted photovoltaic systems are currently recognised in the area statistics as Commercial space classifiedwhich is why they count as settlement and transport areas. With such statistical weaknesses, it is no wonder that the targets are missed. There is a regulatory gap: Areas in solar parks are not sealed and are partly used for agricultural purposes, e.g. in the form of grazing or grassland farming or agri-PV. Professionally maintained solar park areas also serve biodiversity, which requires, for example, mowing and the removal of mown material using agricultural machinery. It therefore makes sense to designate all these solar park areas as Categorise agricultural land and to correct the distorted statistics. Such a categorisation would also have positive effects with regard to the Tax valuationwhich, for example Farm handovers and generational changes on farms plays an important role.
Conclusion
Germany has Sufficient area for the expansion of solar parks, which will only take up 0.3% of Germany's total area by 2030. The areas under and between the rows of modules can be regenerateas they are neither fertilised nor sprayed. In addition, a Agricultural utilisation possible in most cases. Since grassland areas are obviously not commercial areas, it would make sense to categorise professionally managed solar park areas as agricultural land.







